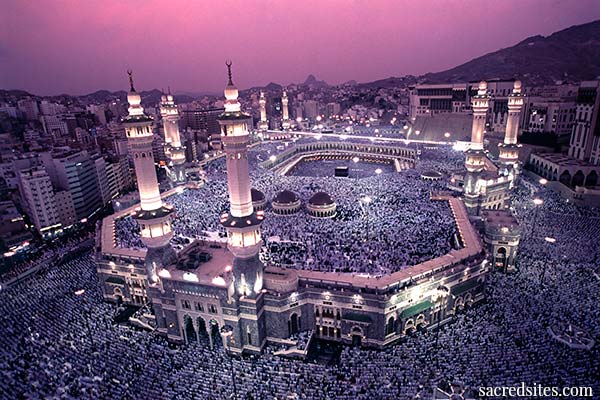
The Great Mosque, Mecca
Mecca (Makkah in Arabic) is the center of the Islamic world and the birthplace of both the Prophet Muhammad and the religion he founded. Located in the Sarat Mountains of central Saudi Arabia and 45 miles inland from the Red Sea port of Jidda (Jeddah), ancient Mecca was an oasis on the old caravan trade route that linked the Mediterranean world with South Arabia, East Africa, and South Asia. By Roman and Byzantine times it had developed into an important trade and religious center, and was known as Macoraba. The sacred land in which Mecca and Medina are located, known as the Hijaz, is the western region of the Arabian peninsula, a narrow tract of land about 875 miles long east of the Red Sea with the Tropic of Cancer running through its center. The land is called Hijaz, meaning barrier, because its backbone, the Sarat Mountains consist of volcanic peaks and natural depressions creating a stark and rugged environment dominated by intense sunlight and little rain fall.
According to ancient Arabian traditions, when Adam and Eve were cast from Paradise they fell to different parts of the earth; Adam on a mountain on the island of Serendip, or Sri Lanka, and Eve in Arabia, on the border of the Red Sea near the port of Jeddah. For two hundred years Adam and Eve wandered separate and lonely about the earth. Finally, in consideration of their penitence and wretchedness, God permitted them to come together again on Mt. Arafat, near the present city of Mecca (previously called Becca or Bakkah, meaning narrow valley). Adam then prayed to God that a shrine might be granted to him similar to that at which he had worshipped in Paradise. Adam's prayers were answered and a shrine was built. (This is a pre-Islamic legend and the Koran, the Islamic Holy Scripture, says nothing whatsoever of Adam's connection with Mecca or of a shrine he prayed at). Adam is said to have died and been buried in Mecca and Eve in Jeddah by the sea which still bears her name, jiddah, meaning maternal ancestor in Arabic.
This shrine passed away during the era of the flood, at which time the body of Adam began to float on the water while the Ark of Noah circumambulated around it and the Ka'ba seven times before journeying north where it landed after the flood. A thousand years later, according to one Islamic tradition in 1892 BC, the great patriarch of monotheism, Abraham, or Ibrahim, came to Mecca with his Egyptian wife Hagar and their child Ishmael. Here Hagar lived with her son in a small house, at the site of the earlier shrine, and Abraham came to visit her occasionally.
Nearly all scholars trace the sanctity of Mecca to the Ka'ba edifice later rebuilt at God's express command by Abraham and Ishmael. Mention must be made, however, of the Zamzan spring and the nearby holy hills of Safa and Marwa (these hills have since disappeared under the leveling topography of modern Mecca). These geographical formations certainly predated the mythical construction of the Ka'ba and could therefore have given birth to the original sanctity of the place. According to Islamic legend, Abraham had left Mecca on God's command, leaving Hagar and Ishmael with only some water and dates. Hagar nursed her son and they drank the remaining water. Soon thereafter, faced with great thirst, Ishmael started to cry and Hagar began to run between the hills of Safa and Marwa looking for water. She repeated the journey seven times until an angel appeared to her, striking the ground with his wing, with the result that the Zamzam spring, which Muslims consider as a tributary of the waters of Paradise, sprang forth. Henceforth Mecca was graced with a source of water which has continued flowing to this day.
After the departure and return of Abraham to Mecca, and his discovery that Hagar had died, Abraham was then ordered by God to make Hagar's house into a temple where people could pray. Therefore, he demolished the house and began construction of the Ka'ba. God gave Abraham precise instructions concerning how to rebuild the shrine and Gabriel showed him the location. It is said that by the grace of God the Divine Peace (al-sakinah) descended in the form of a wind which brought a cloud in the shape of a dragon that revealed to Abraham and Ishmael the site of the old temple. They were told to construct the shrine directly upon the shadow of the cloud, neither exceeding nor diminishing its dimensions. Legends say the shrine was built from the stones of five sacred mountains: Mt. Sinai, the Mount of Olives, Mt. Lebanon, Al-Judi, and nearby Mt. Hira. Upon the completion of the shrine, Gabriel brought a magic stone for the sanctuary. Different sources speculate that this stone was a meteorite or a great white sapphire from the Garden of Eden, that it had been concealed on the nearby sacred mountain of Abu Qubays during the period of the flood, and that it was later restored to Abraham for inclusion in his version of the Ka'ba. Whatever its ultimate origin, the stone was most probably a sacred object of the pre-Islamic Arabian nomads who had settled around the Zamzam spring that flows at the center of old Mecca. Upon completion of the Ka'ba, Abraham and Ishmael, accompanied by the archangel Gabriel, then performed all the elements which constitute the Hajj ritual of today. The Ka'ba they had constructed was destined to become the most important sacred site of the nomadic tribes that inhabited the great Arabian deserts. (Abraham was later to leave Mecca to die in Palestine in al-Khalil).
With the passage of centuries, the original Abrahamic observances at the Ka'ba were progressively diluted by the addition of various pagan elements (these arriving via the caravan routes that led to Mecca). The pilgrims of pre-Islamic times visited not only the house of Abraham and the sacred stone of Gabriel but also the collection of stone idols (representing different deities) housed in and around the Ka'ba. There were said to be 360 different deities including Awf, the great bird, Hubal the Nabatean god, the three celestial goddesses Allat, Aluzza and Manat, and statues of Mary and Jesus. The most important of all these deities, and chief of the Meccan pantheon, was known as Allah (meaning "the god"). Worshipped throughout southern Syria and northern Arabia, and the only deity not represented by an idol in the Ka'ba, Allah would later become the sole god of the Muslims.
The city of Mecca achieved its major religious significance following the birth and life of the Prophet Muhammad (570-632AD). In 630 Muhammad took control of Mecca and destroyed the 360 pagan idols, with the notable exception of the statues of Mary and Jesus. The idol of Hubal, the largest in Mecca, was a giant stone situated atop the Ka'ba. Following the command of the Prophet, Ali (the cousin of Muhammad) stood on Muhammad's shoulders, climbed to the top of the Ka'ba and toppled that idol.
Following his destruction of the pagan idols, Muhammad joined certain of the ancient Meccan rituals with the Hajj pilgrimage to Mt. Arafat (another pre-Islamic tradition), declared the city a center of Muslim pilgrimage and dedicated it to the worship of Allah alone. Muhammad did not, however, destroy the Ka'ba and the sacred stone it housed. Rather, he made them the centerpiece of the Muslim religion based on his belief that he was a prophetic reformer who had been sent by god to restore the rites first established by Abraham that had been corrupted over the centuries by the pagan influences. Thus, by gaining both religious and political control over Mecca, Muhammad was able to redefine the sacred territory and restore Abraham's original order to it.
According to the original words of Muhammad, the Hajj pilgrimage is the fifth of the fundamental Muslim practices known as the 'Five Pillars of Islam'. The Hajj is an obligation to be performed at least once by all male and female adults whose health and finances permit it. The pilgrimage takes place each year between the 8th and 13th days of Dhu al-Hijjah, the 12th month of the Islamic lunar calendar. Before setting out, a pilgrim should redress all wrongs, pay all debts, and plan to have enough money for their journey and the support of their family while away.
As pilgrims undertake the journey they follow in the footsteps of many millions before them. When the pilgrim is about 10 kilometers from Mecca he enters the state of holiness and purity known as Ihram, and dons special garments consisting of two white seamless sheets that are wrapped around the body. Entering the great Mosque in Mecca, the pilgrim first walks seven times around the Ka'ba shrine in a counterclockwise direction; this ritual is called turning, or tawaf. Next, entering into the shrine, the pilgrim kisses the sacred stone. The stone is mounted in a silver frame in the wall, four feet above the ground, in the southeast corner of the shrine. It is of an oval shape about twelve inches in diameter, composed of seven small stones (possibly basalt) of different sizes and shapes joined together with cement. Legend tells that the stone (al-Hajaru al-Aswad, the 'Black Stone') was originally white but became gradually darkened by the kisses of sinful mortals (some traditions say by the sins of 'offsprings of Adam').
During the next few days the pilgrim walks a ritualized route to other sacred places in the Mecca vicinity (Mina, Muzdalifah, Arafat, the Mount of Mercy and Mt. Namira) and returns to the Ka'ba on the final day (the word Hajj probably derives from an old Semitic root meaning 'to go around, to go in a circle'). The plain of Arafat where millions of pilgrims assemble in a vast congregation symbolizes the plain of Mahshar or Resurrection where everyone will stand before God on the Day of Judgement. In the middle of Arafat stands Jabal al-Rahmah or the Mount of Mercy where the last verses of the Koran were revealed and where one of the famous farewell addresses of the Prophet was delivered. It is here that the alchemy of union between various aspects of human nature takes place and where men and women regain their primordial spiritual wholeness, for it was here that Adam and Eve found each other again after their fall to earth from Paradise. At Mina, where the Prophet delivered his last words during his final pilgrimage, pilgrims cast stones against three large stone pillars representing Satan (al-Shaytan) as a symbol of the eternal battle that must be waged against the demons within. Finally there is the sacrifice of an animal, a sheep or a camel, in emulation of Abraham's preparation to sacrifice his son Ishmael.
Once a believer has made the pilgrimage to Mecca men may add the title al-Hajji to their name, hajjiyah for females. In different Islamic countries returning pilgrims will use a variety of signs to indicate they have made the Hajj; these include painting pictures of the Ka'ba (and the pilgrim's means of transportation to the shrine) upon the walls of their homes, painting the entrance doorway of the house bright green, and wearing hats or scarves of green color. A so-called Minor Pilgrimage, known as the Umra, contains some but not all of the rites of the Hajj and may be performed at any time of the year.
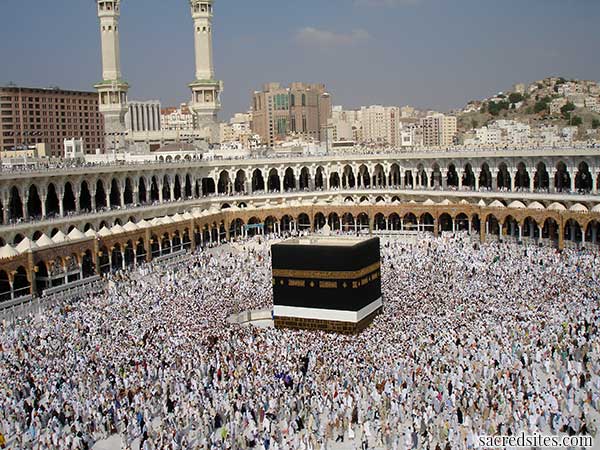

The Ka’ba, The Great Mosque, Mecca
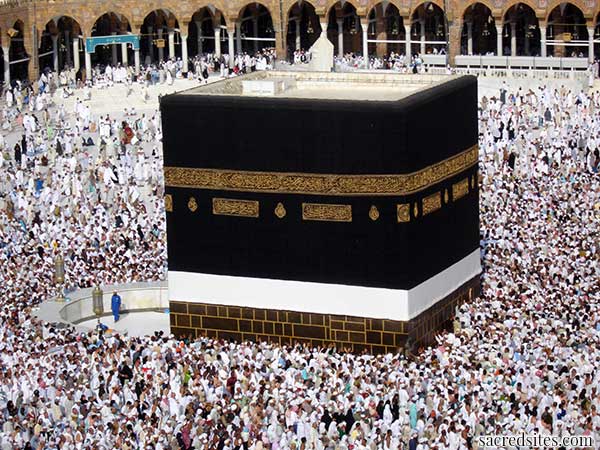

The Ka’ba, The Great Mosque, Mecca
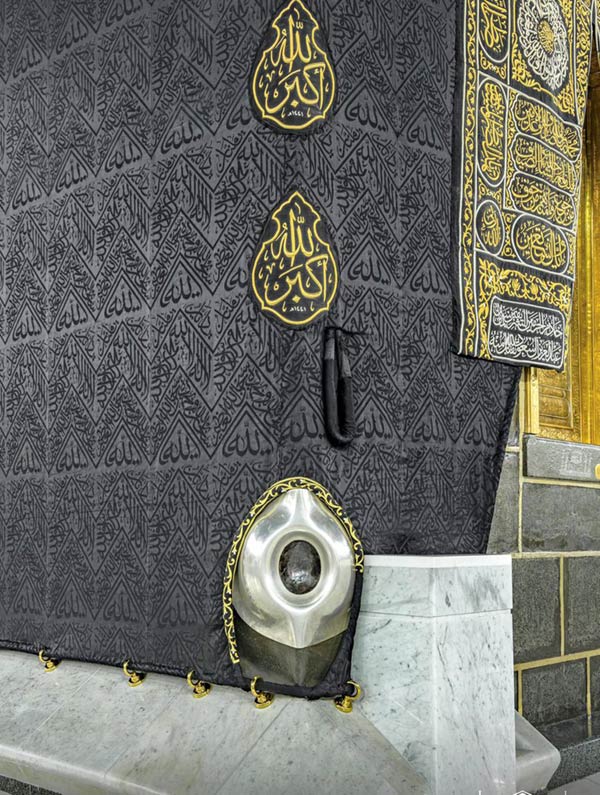

The Black Stone of the Ka’ba.
The area around the Ka'ba was enclosed by a wall in 638 to create a defined space for the tawaf ritual of circumambulation. In 684 the mosque was further enlarged and ornamented with numerous mosaic and marble decorations. In 709 the Umayyad caliph Al-Walid placed a wooden roof upon marble columns to protect the arcades of the mosque, and between 754 and 757 the Abbasid Caliph Al-Mansur carried out further enlargements, including the first minaret. During the next 700 years numerous modifications were carried out although no major alterations to the form of the building occurred until the Ottoman period in the 16th century (in the 10th century the Black Stone was actually stolen for a period of twenty-one years by the Carmathians). Large-scale renovations and remodeling was undertaken in 1564 during the reign of the Ottoman Sultan Sulayman the Magnificent, who rebuilt the minarets and replaced the wooden roofs of the arcades with stone domes. The next major rebuilding of the mosque occurred in the 20th century under the direction of the Saudi royal family and resulted in the Mecca mosque becoming the largest in the world.
The Ka'ba today stands in the midst of an open courtyard known as the al-masjid al-haram, the 'sanctuary'. The cubical (the word Ka'ba means "cube"), flat-roofed building rises fifty feet from a narrow marble base on mortared bases of a local blue-gray stone. Its dimensions are not exactly cubical: the northeastern and southwestern walls are forty feet long, while the other two walls are five feet shorter (12 meters long, 10 meters broad, 16 meters high). The structure's corners, rather than the walls, are oriented toward the compass points. The east and west walls are aligned to the sunrise at the summer solstice and sunset at the winter solstice. The south wall is directed to the rising of the bright star Canopus. The northeastern wall has the only door of the building, about seven feet above the ground level. Inside is an empty room with a marble floor and three wooden pillars supporting the roof. There are some inscriptions on the walls, hanging votive lamps, and a ladder leading up to the roof. The entire Ka'ba structure is draped with a black silk covering, called a kiswa, upon which passages from the Koran are embroidered in gold. The kiswa is renewed every year and the old kiswah is cut up and distributed so as to allow the barakah of the ka'ba to emanate among those to whom the pieces of the cloth are given. During the early centuries of Islamic history the kiswah was made in Egypt and carried with great ceremony to Mecca but now it is fashioned near the holy city itself.
Opposite the northwestern wall of the Ka'ba is an area of special sanctity called the Hijr, which Muslim tradition identifies as the burial place of Hagar and Ishmael (and here, too, Ishmael had been promised by God that a gate into heaven would be opened for him). In Muhammad's time, the Hijr was a place used for discussion, prayer and, significantly, for sleep. The sleepers in the Hijr appear to have gone there specifically to have dreams of divine content: Muhammad's grandfather, Abd al-Muttalib, was inspired to discover the Zamzam well while sleeping there; the mother of the Prophet had a vision of her son's greatness; and at the Hijr Muhammed himself was visited by Gabriel before beginning his miraculous Night Journey to Jerusalem.
The Ka'ba, the Zamzan well, the Hijr and the hills of Safa and Marwa are now all enclosed in a vast structure called the Haram al-Sharif, 'The Noble Sanctuary'. Ringed by seven towering minarets and sixty-four gates, this truly monumental building has 160,000 yards of floor space, is capable of holding more than 1.2 million pilgrims at the same time, and is the largest mosque in the Islamic world. The sa'y, or ritual walk between the hills of Safa and Marwa, celebrating the rapid movement of Hagar and her son Ishmael in search of water and being an integral part of the Hajj rituals, is understood to represent man's quest in this world for the life-bestowing bounties of God.
It is interesting to note that prior to the age of the European world explorations, the pilgrimage to Mecca was the single largest expression of human mobility. As the religion of Islam rapidly spread across the world from Indonesia and China in the Far East to Spain, Morocco and West Africa in the west, ever increasing numbers of pilgrims made the long, and often dangerous, journey to Mecca. Some came by boat, braving the Red Sea, the Black Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, the Arabian Sea and the Persian Gulf. Others spent months in camel caravans slowly crossing great tracts of land. The most important pilgrimage caravans were the Egyptian, the Syrian, the Maghribi (the trans-Saharan route), the Sudanese (the sub-Saharan, savanna route), and those from Iraq and Persia.
Forbidden to persons not of the Muslim faith, Mecca came to symbolize for Europeans the secrets and mysteries of the orient, and as such became a magnet for explorers and adventurers. A few of these daring travelers, such as John Lewis Burckhardt from Switzerland (who, in 1812, was also the first European to visit the ruins of Petra) and Sir Richard Burton from Great Britain were able to convincingly impersonate Muslim pilgrims, gain entrance to Mecca, and write wonderfully of the holy city upon their return to Europe. Other explorers were neither so lucky nor divinely guided; many of them disappeared or were caught and sold into slavery. To this day, Mecca remains strictly closed for persons not of the Muslim faith.
Nowadays approximately 2,000,000 people perform the Hajj each year, and this pilgrimage serves as a unifying force in Islam by bringing together followers from diverse countries and language groups. In a certain sense, however, Mecca is said to be visited by all devout and practicing Muslims every day. This is because five times each day (three times in the Shi'a sect) millions upon millions of believers perform their prayers (bowing and prostrating in a specific sequence of movements) in the direction of Mecca. Wherever the place of prayer - in a mosque, a remote place in the wilderness or the interior of a home - Muslims face towards Mecca and are united to the Ka'ba by an invisible line of direction called the qibla.
Readers interested in more detailed information about Mecca and the great Muslim pilgrimage will enjoy the excellent writings of Michael Wolfe and F.E. Peters, listed in the bibliography. The two other most important sacred sites for Muslims are the Prophets Mosque in Medina and the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem.
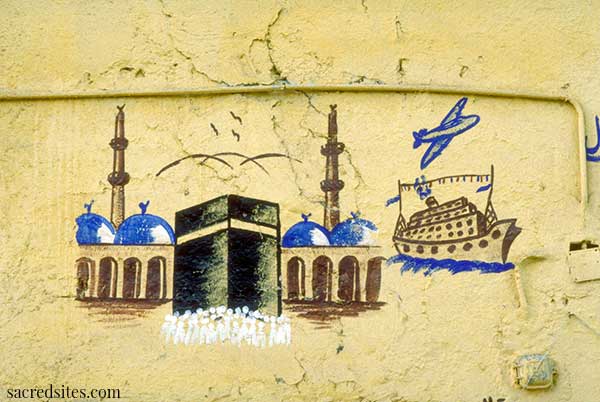

Paintings (on houses in Egypt) of the Ka'ba, Islam's most sacred shrine in Mecca
Additional notes on Mecca
On the walls of ordinary houses all over Egypt, one can still see colorful two-dimensional mementos of the sacred journey to Mecca. A lively tradition of domestic mural painting has preserved a formulaic combination of inscriptions and images of the Ka'ba and of the Prophet's mosque. Images usually show the various modes of travel to the holy places, typically including planes, trains, ships, camels, and often depict the pilgrim on a prayer carpet. These murals serve a protective purpose in addition to certifying publicly and proudly that the house's inhabitants are due the special status and prestige accorded to those who have accomplished the hajj and received the honorific title of hajji. It is especially significant that family and friends of the pilgrim execute the paintings while the travelers are away, so that the dwelling undergoes its ritual transformation even as its inhabitants do.
Seven Doors to Islam: Spirituality and the Religious Life of Muslims, by John Renard
Folklore notes on Adam
Adam was formed by god out of a handful of dust taken, according to tradition, from the Holy Rock of Sakhrah in Beyt el Maddas. When god formed Adam He left the figure lying lifeless for forty days, some say forty years, while notice was given to the Angels and the Jinn to be ready to worship him as soon as god put breath into his nostrils. At first Adam was male and female in one body, man on one side and female on the other. In due time the female part separated from the male and became a complete woman. Adam and the woman mated but they were not happy as the female refused to submit to Adam, saying that as they were made from the same dust, he had no right to order her about. So she was turned out of Paradise and, consorting with Iblis (Satan), became the mother of devils. She is called El-Karineh by the Arabs, both Christian and Muslim, and Lilith by the Jews (La Brusha by the Sephardim Jews). She is the deadly enemy of all women, especially those who have recently become mothers. When El-Karineh was driven out of Paradise, god created Eve out of one of Adam's ribs, which had been extracted while he slept. Adam and Eve were happy together until Satan succeeded in getting back into Paradise concealed in a serpent's fangs. Once there, Satan persuaded Eve to eat of the forbidden fruit. Adam, having been persuaded by his wife to share her offense, was, as a punishment, cast out of Paradise together with Eve, Satan and the Serpent. All four of them fell to the earth, each coming to a different place: Adam at Serendib or Ceylon; Eve at Jiddah; Satan at Akabah; and the Serpent at Isfahan in Persia. Two hundred years passed before Adam and Eve met once more at Jebel Arafat, the mountain of Recognition, near Mecca. During these two hundred years, Eve had borne offspring of the seeds of devils and Adam had many children by female Jinns.

Painting of the Ka'ba, Mecca
Additional notes on Pilgrimage and Sacred sites in Islam
The worship of saints or even of the Prophet Muhammad himself is blasphemy according to Islamic orthodoxy. When Muhammad died, he was buried in the house of his wife Aisha and it was forbidden to visit his corpse. In accordance with his teachings, no special treatment was given to the burial places of the four rightly guided Caliphs or the Umayyads or early Abbasids, and no special buildings of any importance were erected over any of their graves.
After the ninth century the veneration of tombs of pious men became popular, especially in eastern Iran, and the memorial tomb with religious or secular connotations assumed a leading place among the types of monumental buildings in Islamic architecture. Clearly the urge to build tombs owed nothing to Islamic dogma but rested on deep-seated popular belief.
The grave of a saint (awliya) is a point of psychic contact with the saint for the tomb is conceived as the dwelling place of the saint. These shrines, in different parts of the Islamic world may be called mashhad, maqam, ziyarat (Morocco), imamzada (Iran), mazar (Central Asia) and qabiristan (India) and they may be compared in function to the Christian martyrium.
Apart from the altruism involved in building a mosque, anyone who plans to include his tomb within the area of the mosque expects that this action will ensure the maintenance of his tomb, as it is integral to the architecture of the mosque, and also that his burial remains will benefit supernaturally from the prayers of the users of the mosque and also by the baraka that is generated every time the Koran is recited.
The concept of the living saint is extremely important in Islam. Pilgrims visit the shrine of a saint to receive his baraka and seek his intercession, shafa'a. .. On leaving a shrine, a pilgrim is careful not to turn his or her back on the cenotaph of the saint.
A coffin is optional, but a vault, no matter how simple, is indespensible, for the fact that the body must be able to sit up and reply to the Angels of the Grave, known as Munkir and Nakir, who question it on the first night after burial. ..Bodies are buried in the recumbent posture at right angles to the qibla (the direction of prayer towards Mecca) in such a way that they would face Mecca if turned on their side. This way the believer has the same physical relationship with Mecca in both life and death.
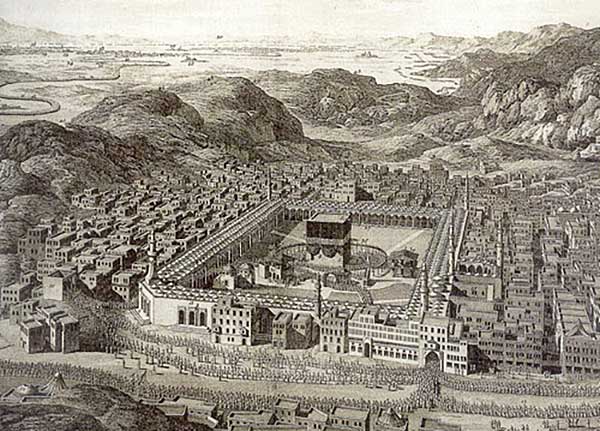

The Hajj pilgrimage to the Ka'ba in antiquity. At the bottom of the drawing notice the line of pilgrims entering the front of the Great Mosque. In the upper left corner of the drawing that line may be seen extending for many miles into the distance.
Sunni / Shia Distribution in the Middle East
 Martin Gray is a cultural anthropologist, writer and photographer specializing in the study of pilgrimage traditions and sacred sites around the world. During a 40 year period he has visited more than 2000 pilgrimage places in 165 countries. The World Pilgrimage Guide at sacredsites.com is the most comprehensive source of information on this subject.
Martin Gray is a cultural anthropologist, writer and photographer specializing in the study of pilgrimage traditions and sacred sites around the world. During a 40 year period he has visited more than 2000 pilgrimage places in 165 countries. The World Pilgrimage Guide at sacredsites.com is the most comprehensive source of information on this subject.Also consult:
Non-Hajj Pilgrimage in Islam: A Neglected Dimension of Religious Circulation; Bhardwaj, Surinder M.; Journal of Cultural Geography, vol. 17:2, Spring/Summer 1998
Sufism: Its Saints and Shrines: An Introduction to the Study of Sufism with Special Reference to India; Subhan, John A.; Samuel Weiser Publisher; New York; 1970